开始
LCEL 可以轻松地从基本组件构建复杂的链,并支持开箱即用的功能,例如流式传输、并行性和日志记录。
基本示例:prompt+模型+输出解析器
最基本和常见的用例是将提示模板和模型链接在一起。为了看看这是如何工作的,让我们创建一个接受主题并生成笑话的链:
pip install --upgrade --quiet langchain-core langchain-community langchain-openai
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("tell me a short joke about {topic}")
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4")
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
chain = prompt | model | output_parser
chain.invoke({"topic": "ice cream"})
"Why don't ice creams ever get invited to parties?\n\nBecause they always drip when things heat up!"
请注意这行代码,我们使用 LCEL 将不同的组件拼凑成一个链:
chain = prompt | model | output_parser
|符号类似于 unix 管道运算符,它将不同的组件链接在一起,将一个组件的输出作为下一个组件的输入。
在此链中,用户输入传递到提示模板,然后提示模板输出传递到模�型,然后模型输出传递到输出解析器。让我们分别看一下每个组件,以真正了解发生了什么。
1. Prompt
Prompt 是一个 BasePromptTemplate,这意味着它接受模板变量的字典并生成 PromptValue。 PromptValue 是完整提示的包装器,可以传递给 LLM(将字符串作为输入)或 ChatModel(将一系列消息作为输入)。它可以与任何一种语言模型类型一起使用,因为它定义了生成 BaseMessage 和生成字符串的逻辑。
prompt_value = prompt.invoke({"topic": "ice cream"})
prompt_value
ChatPromptValue(messages=[HumanMessage(content='tell me a short joke about ice cream')])
prompt_value.to_messages()
[HumanMessage(content='tell me a short joke about ice cream')]
prompt_value.to_string()
'Human: tell me a short joke about ice cream'
2. 模型
然后将 PromptValue 传递给模型。在本例中,我们的模型是 ChatModel,这意味着它将输出 BaseMessage。
message = model.invoke(prompt_value)
message
AIMessage(content="Why don't ice creams ever get invited to parties?\n\nBecause they always bring a melt down!")
如果我们的模型是 LLM,将会输出字符.
from langchain_openai.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct")
llm.invoke(prompt_value)
'\n\nRobot: Why did the ice cream truck break down? Because it had a meltdown!'
3. 输出解析
最后,我们将模型输出传递给 output_parser,它是一个 BaseOutputParser,这意味着它接受字符串或 BaseMessage 作为�输入。 StrOutputParser 特别简单地将任何输入转换为字符串。
output_parser.invoke(message)
"Why did the ice cream go to therapy? \n\nBecause it had too many toppings and couldn't find its cone-fidence!"
4. 整个管道
按照以下步骤操作:
- 我们将所需主题的用户输入传递为
{"topic": "ice Cream"} - 提示组件接受用户输入,然后在使用主题构造提示后使用该输入构造 PromptValue。
- 模型组件采用生成的提示,并传递到 OpenAI LLM 模型进行评估。模型生成的输出是 ChatMessage 对象。
- 最后,output_parser 组件接收 ChatMessage,并将其转换为 Python 字符串,该字符串从 invoke 方法返回。

请注意,如果您对任何组件的输出感到好奇,您始终可以测试链的较小版本,例如提示或提示 |模型以查看中间结果:
input = {"topic": "ice cream"}
prompt.invoke(input)
# > ChatPromptValue(messages=[HumanMessage(content='tell me a short joke about ice cream')])
(prompt | model).invoke(input)
# > AIMessage(content="Why did the ice cream go to therapy?\nBecause it had too many toppings and couldn't cone-trol itself!")
RAG 搜索例子
对于我们的下一个示例,我们希望运行检索增强生成链以在回答问题时添加一些上下文。
# Requires:
# pip install langchain docarray tiktoken
from langchain_community.vectorstores import DocArrayInMemorySearch
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableParallel, RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_openai.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_openai.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
vectorstore = DocArrayInMemorySearch.from_texts(
["harrison worked at kensho", "bears like to eat honey"],
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
template = """Answer the question based only on the following context:
{context}
Question: {question}
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
model = ChatOpenAI()
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
setup_and_retrieval = RunnableParallel(
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
)
chain = setup_and_retrieval | prompt | model | output_parser
chain.invoke("where did harrison work?")
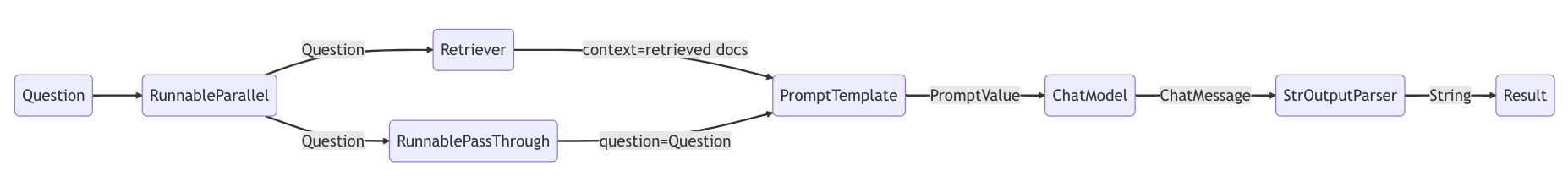
在这种情况下,组成的链是:
chain = setup_and_retrieval | prompt | model | output_parser
为了解释这一点,我们首先可以看到上面的提示模板将上下文和问题作为要在提示中替换的值。在构建提示模板之前,我们希望检索与搜索相关的文档并将它们作为上下文的一部分包含在内。
作为初步步骤,我们使用内存存储设置检索器,它可以根据查询检索文档。这也是一个可运行的组件,可以与其他组件链接在一起,但您也可以尝试单独运行它:
retriever.invoke("where did harrison work?")
然后,我们使用 RunnableParallel 通过使用检索到的文档的条目以及原始用户问题来准备提示中的预期输入,使用检索器进行文档搜索,并使用 RunnablePassthrough 传递用户的问题:
setup_and_retrieval = RunnableParallel(
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
)
回顾一下,完整的链是:
setup_and_retrieval = RunnableParallel(
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
)
chain = setup_and_retrieval | prompt | model | output_parser
流程是:
- 第一步创建一个包含两个条目的 RunnableParallel 对象。第一个条目上下文将包括检索器获取的文档结果。第二个条目问题将包含用户的原始问题。为了传递问题,我们使用 RunnablePassthrough 来复制此条目。
- 将上述步骤中的字典提供给提示组件。然后,它采用作为问题的用户输入以及作为上下文的检索到的文档来构造提示并输出 PromptValue。
- 模型组件采用生成的提示,并传递到 OpenAI LLM 模型进行评估。模型生成的输出是 ChatMessage 对象。
- 最后,output_parser 组件接收 ChatMessage,并将其转换为 Python 字符串,该字符串从 invoke 方法返回。
下一步
我们建议阅读接下来的“为什么使用 LCEL”部分,以查看使用和不使用 LCEL 生成通用功能所需的代码的并排比较。